Volume 5, Issue 4 (2025) – 2 articles
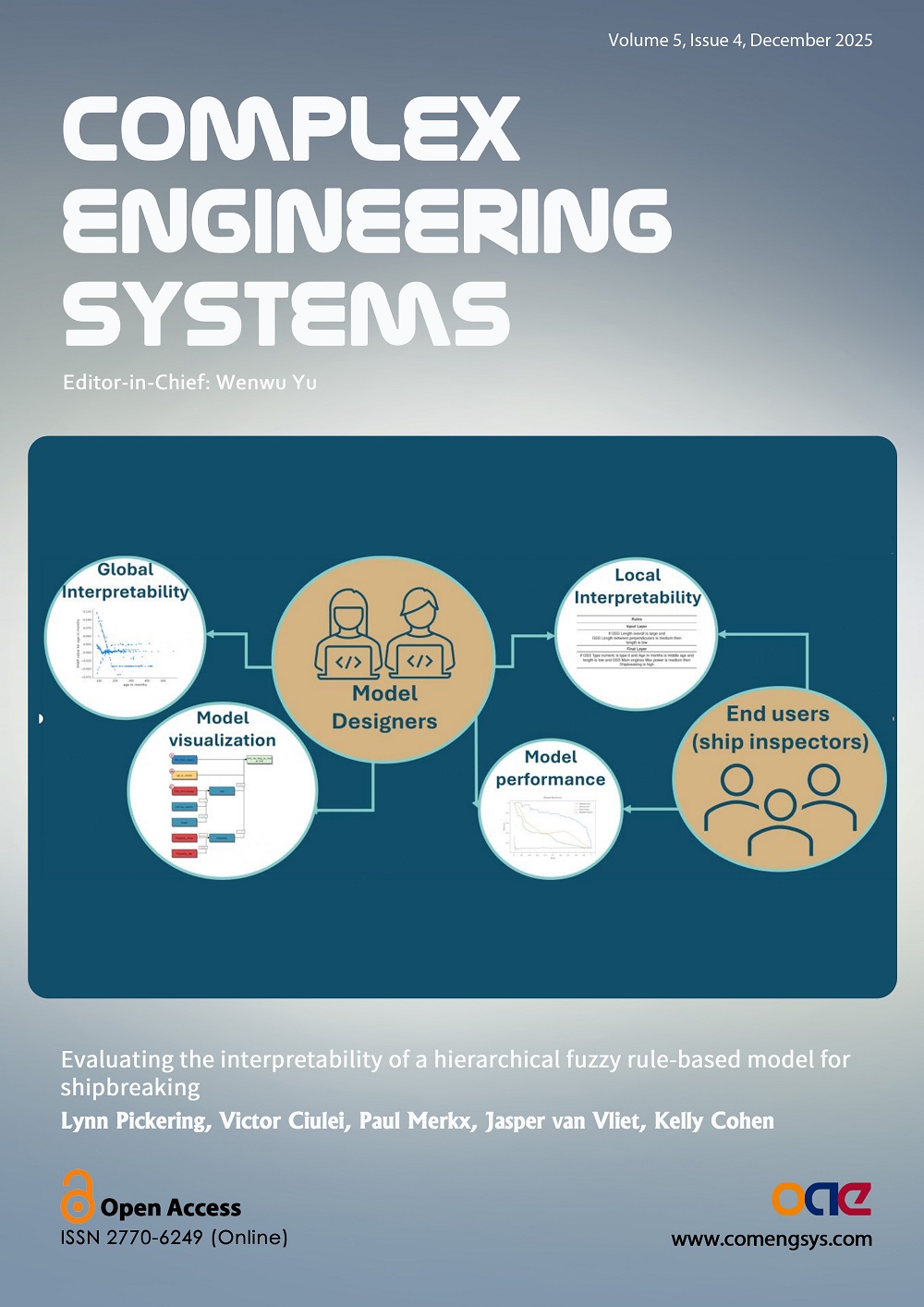
Cover Picture: This paper explores the use of post-hoc model interpretability methods in combination with an intrinsically interpretable model design to create a model that is interpretable to both a model designer and a model end user. A hierarchical fuzzy rule-based model is trained with a genetic algorithm on a real-world shipbreaking use case and the performance-interpretability trade-off of the model with respect to a random forest model is discussed. Further, an interesting pattern was found using the post-hoc interpretability method SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP), with potential implications for the future design of hierarchical fuzzy rule-based models.
view this paper