Topic: Molecular Targets for CCA Therapy
A Special Topic of Hepatoma Research
ISSN 2454-2520 (Online) 2394-5079 (Print)
Submission deadline: 31 Mar 2025
Guest Editor
Special Topic Introduction
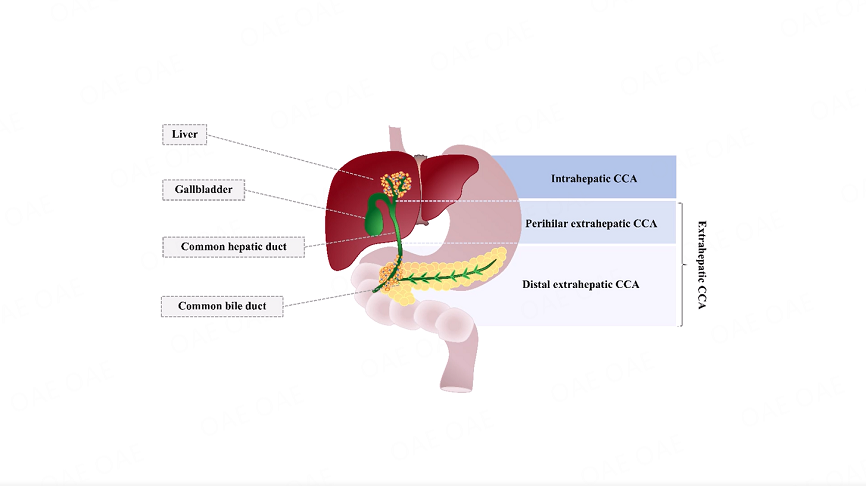
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is a highly aggressive and heterogeneous malignancy of the bile duct with a poor prognosis. The incidence of CCA has been steadily increasing over the past 50 years. Surgery remains the only curative therapy; however, patients are frequently diagnosed at advanced stages, and relapsed rates are high even among those who undergo surgery. Conventional chemotherapies, such as gemcitabine, cisplatin or 5-FU, and radiotherapy, do not offer a cure but merely extend survival. The traditional classification of CCA is based primarily on anatomical location (intrahepatic, perihilar, and distal) or pathological features, which do not provide insight into the underlying mechanisms or potential therapeutic targets. Recently, a novel classification system based on genomic, epigenomic, and transcriptomic analyses has been proposed (Cancer Discov 7:1116, 2017). This new classification divides CCA into four clusters based on mutations, copy numbers, gene expression, and methylation. These advancements have led to the identification of new therapeutic targets and the development of molecularly targeted agents with favorable safety profiles. Clinical trials targeting isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 (IDH1/2) mutations, Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) 2, and HER2 are ongoing and have shown promising results in Phase II/III studies. Additionally, research into the immunological characteristics of CCA, as well as the tumor microenvironment, is paving the way for novel therapeutic strategies. Cancer stem cells, which are capable of initiating tumors and driving malignant growth, are frequently implicated in relapse and acquired resistance to treatment. Novel targeted therapies to eradicate cancer stem cells may help overcome treatment resistance in CCA and reduce relapse and recurrence rates.
This Special Issue focuses on novel molecular targeting therapies for overcoming resistance to such therapies, innovations in CCA treatment, and future perspectives.
Potential topics include, but are not limited to, the following:
1. Targeting Cancer stem cells;
2. CAR-T therapy;
3. Novel antibody therapies: Bi-specific T-cell engaging antibody (BiTE), Tri-specific killer engagers (TriKEs) , etc.;
4. Antibody-drug conjugate for molecular targeting therapy;
5. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs);
6. Therapeutic targeting of tumor metabolism;
7. Targeting tumor microenvironment in cholangiocarcinoma;
8. Radiotherapy and abscopal effects;
9. Radioimmunotherapy;
10. Cancer epigenetics: implications for novel therapeutic strategies;
11. Application of liquid biopsy for molecular targeting therapy;
12. Targeting transcription factors for cancer therapy;
13. Natural products for molecular targeting therapy.
Submission Deadline
Submission Information
For Author Instructions, please refer to https://www.oaepublish.com/hr/author_instructions
For Online Submission, please login at https://www.oaecenter.com/login?JournalId=hr&IssueId=hr2501312167
Submission Deadline: 31 Mar 2025
Contacts: Daisy Zhao, Assistant Editor, Journaleditor@hrpublishing.net